How LNG Storage Tanks Works?
Introduction
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) plays a vital role in supplying clean energy across the world. Once natural gas is cooled and converted into liquid form, it must be stored safely before transportation or regasification. This is where LNG storage tanks come in. These tanks are specially designed to keep LNG extremely cold and safe for long periods.
In this article, we’ll explain how LNG storage tanks work, their design, and their safety features in a simple and clear way.
What Is an LNG Storage Tank?
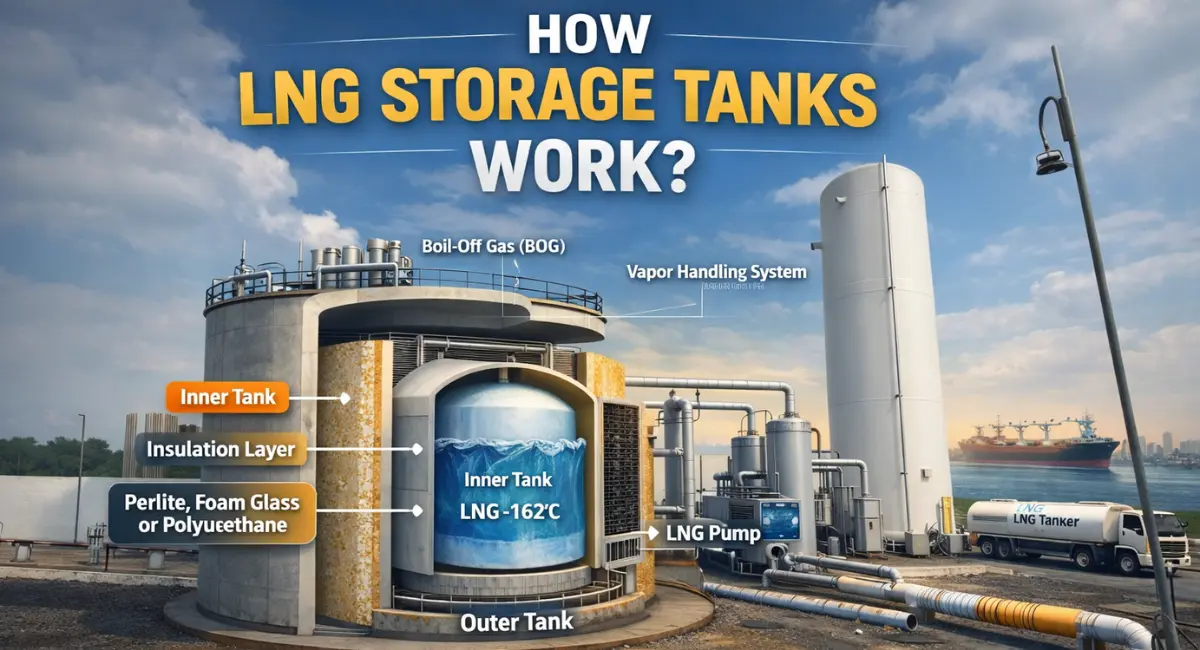
An LNG storage tank is a large, insulated container used to store liquefied natural gas at a very low temperature of about -162°C. At this temperature, natural gas stays in liquid form, taking up much less space than gas.
These tanks are commonly found at:
- LNG import terminals
- Export terminals
- Regasification plants
- LNG peak-shaving facilities
Why Special Tanks Are Needed for LNG
LNG cannot be stored in normal tanks because:
- It is extremely cold
- It must stay liquid
- Safety is critical due to flammability
So, LNG tanks are designed to:
- Maintain cryogenic temperatures
- Minimize heat entry
- Prevent leaks
- Handle pressure safely
Basic Structure of LNG Storage Tanks
Most LNG storage tanks have two main walls:
1. Inner Tank
- Made of nickel steel or stainless steel
- Directly holds the LNG
- Can withstand very low temperatures
2. Outer Tank
- Made of reinforced concrete or steel
- Provides structural strength
- Acts as secondary containment in case of leakage
Insulation Layer
- Located between inner and outer tanks
- Made of perlite, foam glass, or polyurethane
- Prevents heat from entering the tank
In some cases, bentonite can also be used as an insulating material. However, perlite is more widely preferred than bentonite because it offers better thermal performance, higher adaptability to cryogenic conditions, and long-term stability in LNG storage applications.
How LNG Storage Tanks Work – Step by Step
Step 1: LNG Enters the Tank
After liquefaction, LNG is transferred into the storage tank through insulated pipelines. The flow is controlled carefully to avoid sudden temperature or pressure changes.
Step 2: Temperature Is Maintained
The thick insulation keeps the LNG at -162°C, reducing heat transfer from outside. This helps keep LNG in liquid form.
Step 3: Boil-Off Gas Is Managed
A small amount of LNG may evaporate due to slight heat entry. This vapour is called Boil-Off Gas (BOG).
- BOG is collected
- Re-liquefied or
- Used as fuel within the plant
This prevents pressure build-up inside the tank.
Step 4: Pressure Control
Pressure inside the tank is monitored continuously. Safety valves and control systems ensure pressure remains within safe limits.
Step 5: LNG Withdrawal
When LNG is needed:
- It is pumped out of the tank
- Sent to vaporizers
- Converted back into gas for pipelines
Types of LNG Storage Tanks
- Single containment tanks
- Double containment tanks
- Full containment tanks (most common and safest)
Full containment tanks can safely hold LNG even if the inner tank fails.
Vertical vs Horizontal LNG Storage Tanks
Does the Orientation of an LNG Storage Tank Matter?
Yes, it really matters.
Sometimes people ask, “Why are some LNG tanks vertical and others horizontal?”
You might also wonder why large LNG terminals always use tall tanks, while LCNG stations use long, bullet-shaped tanks.
The difference is not random. The orientation of an LNG storage tank affects safety, storage capacity, land usage, cost, and boil-off gas handling. Let’s understand this in a simple way.
LNG storage tanks can be installed in vertical or horizontal orientation depending on capacity, application, and site conditions.
Vertical LNG Storage Tanks
Most large LNG terminals use vertical tanks.
Key Features:
- Large storage capacity
- Cylindrical, upright design
- Used in import/export terminals and regasification plants
Advantages:
- Suitable for very large volumes of LNG
- Better thermal efficiency
- Smaller land footprint for high capacity
- Easier pressure and boil-off gas management
Disadvantages:
- Higher construction cost
- Complex foundation and civil work
- Longer construction time
Horizontal LNG Storage Tanks
Commonly used in LCNG stations, satellite LNG stations, and small-scale LNG storage.
Key Features:
- Bullet-shaped tanks
- Mounted horizontally on saddles
- Smaller storage volumes
Advantages:
- Lower cost
- Faster installation
- Easier transportation and installation
- Ideal for small or mobile LNG facilities
Disadvantages:
- Limited storage capacity
- Requires more land area for higher volumes
- Less efficient boil-off gas handling compared to vertical tanks
Vertical vs Horizontal – Quick Comparison
| Feature | Vertical Tank | Horizontal Tank |
|---|---|---|
| Storage Capacity | Very high | Low to medium |
| Typical Use | LNG terminals | LCNG & satellite stations |
| Land Requirement | Less for large volume | More for same volume |
| Construction Cost | High | Lower |
| Installation Time | Long | Short |
| BOG Management | More efficient | Less efficient |
If you want to know more about LNG vs CNG vs PNG What is the diffrence?
Safety Features of LNG Storage Tanks
LNG storage tanks are built with multiple safety systems:
- Gas detection sensors
- Emergency shutdown systems
- Pressure relief valves
- Fire and spill protection systems
- Continuous monitoring and alarms
These features make LNG storage extremely safe when properly operated.
Advantages of LNG Storage Tanks
- Safe long-term storage
- Efficient use of space
- Minimal gas losses
- High safety standards
- Supports global LNG supply chain
Conclusion
LNG storage tanks are engineering marvels designed to safely store liquefied natural gas at ultra-low temperatures. With strong materials, advanced insulation, and multiple safety systems, these tanks play a crucial role in LNG terminals worldwide.
Understanding how LNG storage tanks work helps us appreciate the technology behind modern energy systems.
Apart from large EPC players, India also has specialised cryogenic tank manufacturers such as INOXCVA, VRV Asia, CRYOGAS Industries, and Beerens Gas,denEB solutions & Bhiwadi cylinders, which focus on LNG, LCNG, and industrial cryogenic storage solutions.
One thought on “How LNG Storage Tanks Works?”